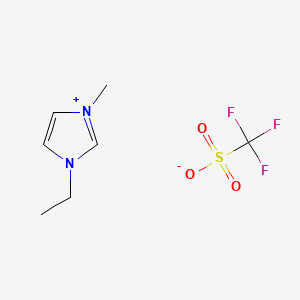


[EMIM][OTf]
CAS No.: 145022-44-2
- Molecular Formula: C7H11F3N2O3S
- Molecular Weight: 260.24 g/mol
Chemical type
- Imidazolium-based ionic liquid (IL)
- Ionic liquid (imidazolium-based)
Key properties
- [EMIM]⁺ cation promotes CO₂RR similar to [BF₄] counterpart
- [OTf]⁻ anion chemically binds to undercoordinated Mo sites (via CF₃ group), poisoning active sites
- Leads to surface passivation and deactivation for CO₂RR
- High affinity for HER promotion when sites are blocked
- Stable structure but aggressive anion interaction
- Hydrolytically stable
- Thermally and electrochemically stable
- Does not crystallize under high pressure (up to 10 GPa)
- Crystallizes upon cooling (around 220–200 K)
- Anion resides above imidazolium plane with C2–O distance ≈ 2.23 Å
- Potential co-catalyst for CO₂RR, but results in exclusive H₂ production due to poisoning
- Electrolyte for studying anion effects in catalysis
- Reaction medium (alternative to hydrolytically unstable PF₆⁻ and BF₄⁻ salts)
- Electrolyte component for electrochemical cells
- Potential use in heat transfer materials and lubricants
- Polymerization of methyl methacrylate (high molecular weight)
Classification by use
- Electrolyte components for electrochemical systems
- Co-catalysts for comparative studies in reaction selectivity
- Chemicals used as electrolytes
- Chemicals used as reaction media/solvents
- Chemicals used in polymer production
- [1] Influence of ionic liquid anions on electrochemical CO2 reduction to higher hydrocarbons on sulfur-vacant MoS2, Applied Catalysis O: Open, Volume 210, January 2026, 207083
- [2] Temperature and Pressure Dependence of the Infrared Spectrum of 1-Ethyl-3-Methylimidazolium Trifluoromethanesulfonate Ionic Liquid, Appl. Sci., 2020, 10(12), 4404