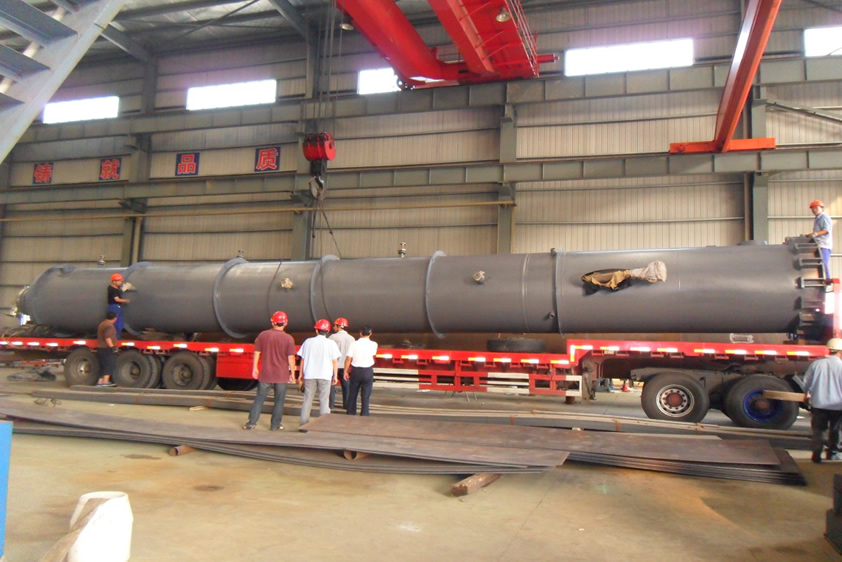
Crude benzene hydrogenation main reactor
No.: Demei-M-R-004
- Operating Pressure: 2.5 – 6.0 MPa
- Hydrogen-to-Benzene Ratio (H₂/Benzene): 200:1 – 600:1 (volume ratio)
- Space Velocity (LHSV): 1 – 3 h⁻¹
- Equipment Type: Vertical fixed-bed reactor
- Temperature: 280–350 °C (Inlet approximately 280 °C, outlet approximately 350 °C)
- Catalyst: Co-Mo based (γ-Al₂O₃ support, flake or rod-shaped, generally two layers)
- Liquid Hourly Space Velocity (LHSV): 0.5–1.0 h⁻¹
- Material: Shell 14Cr1MoR/12Cr2Mo1R + inner wall 0Cr18Ni10Ti overlay welding
- Example Specifications: φ3200 mm × 18000 mm, single unit catalyst loading ≈ 40 t, annual processing capacity of crude benzene 100,000–200,000 tons
- Bed Pressure Drop: ≤0.25 MPa
- Design Temperature/Pressure: 400 °C / 4.0 MPa (meeting a 1.5 times safety factor)
- Structure: Axial flow, double catalyst bed, with cold hydrogen pipes between beds, top inlet distributor + outlet collector, bottom head with discharge port
- Design Life: ≥10 years
The crude benzene hydrogenation main reactor is a continuous fixed-bed hydrogenation reactor operating under high temperature and medium pressure. The feedstock (light benzene, after diolefins and styrene have been removed in a pre-reactor) is mixed with recycled hydrogen and flows from top to bottom through a Co-Mo catalyst bed, completing desulfurization, denitrification, deoxygenation, and olefin saturation reactions. To control the exothermic temperature rise, cold hydrogen is injected between the catalyst beds; the shell is made of chromium-molybdenum steel with a stainless steel lining, and the internal components utilize a high-performance distribution, collection, and cold hydrogen system to ensure uniform fluid flow, low pressure drop, and long operating cycles.
-
Removes sulfur compounds such as thiophene, mercaptans, and dibenzothiophene, generating H₂S which then enters the tail gas treatment system;
-
Removes nitrogen compounds such as pyridine and quinoline, generating NH₃;
-
Removes oxygen compounds such as phenols and dibenzofuran, generating H₂O;
-
Hydrogenates and saturates residual olefins, diolefins, and styrene to prevent coking in the subsequent extraction and distillation system;
-
Provides "sulfur-free, low-olefin, low-color" hydrogenated oil for subsequent extraction and distillation, thereby obtaining high-purity benzene, toluene, and xylene products.
- Factory Condition: Manufactured as a whole or in sections, subjected to non-destructive testing, heat treatment, and hydrostatic testing, and coated with anti-corrosion paint on the surface.
- Transportation Method: Transported by heavy-duty flatbed trucks or modular sea transport (oversized equipment requires special permits).
- Protective Measures:
- Internal nitrogen purging to prevent oxidation or moisture damage to the catalyst bed;
- Blind flanges installed on flange openings to prevent foreign objects from entering;
- Outer surface wrapped with waterproof canvas or plastic film.