Your Location:Home > Products > Pharmaceutical Raw Material > Warfarin sodium


CasNo: 129-06-6
MF: C19H16NaO4
Appearance: white or yellowish powder
Warfarin sodium, a coumarin oral anticoagulant, exerts its anticoagulant effect by inhibiting vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors. It is commonly used clinically to prevent and treat thromboembolic diseases, such as thrombosis caused by atrial fibrillation and post-heart valve replacement surgery. The therapeutic window of warfarin sodium is narrow and there are large individual differences. When using it, it is necessary to closely monitor coagulation indicators, such as the international normalized ratio (INR), to adjust the dosage to achieve the ideal anticoagulant effect. Warfarin sodium is usually prepared by a specific chemical synthesis method and is one of the important drugs in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
InChI:InChI=1/C19H16O4.Na/c1-12(20)11-15(13-7-3-2-4-8-13)17-18(21)14-9-5-6-10-16(14)23-19(17)22;/h2-10,15,21H,11H2,1H3;/q;+1
Interactions of warfarin with other drugs or substances can pose a serious problem. We assessed three drug information compendia—Clinical Pharmacology, ePocrates, and Micromedex—and the warfarin sodium (Coumadin) product label (August 2007) approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for listings of interactions between warfarin and drugs, biologics, foods, and dietary supplements.
Nine patients taking warfarin had bleeding complications (which were major in three patients), as compared with one patient taking heparin (P = 0.008). Our data indicate that adjusted-dose subcutaneous heparin therapy provides an effective alternative to warfarin sodium and is associated with a lower risk of bleeding.
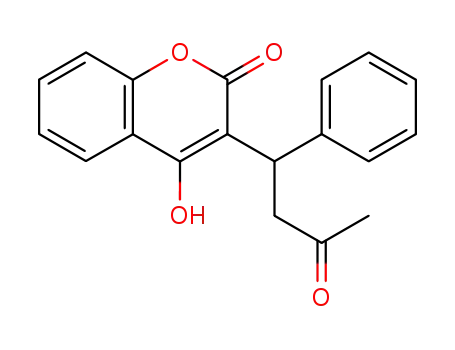
warfarin

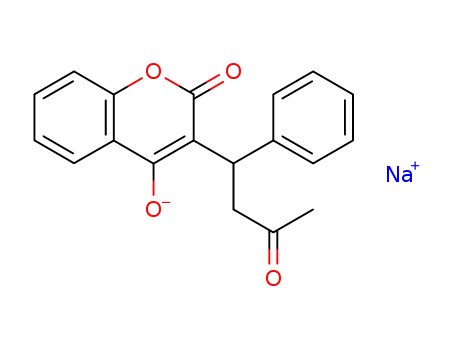
warfarin
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With sodium hydroxide; In water; at 25 - 55 ℃; for 2h; Product distribution / selectivity;
|

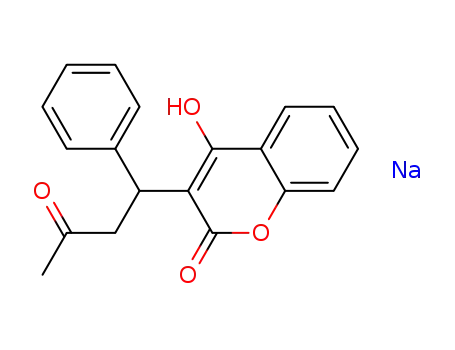
warfarin sodium
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
|
29 g(88%) |
|
|
|
|
|

warfarin
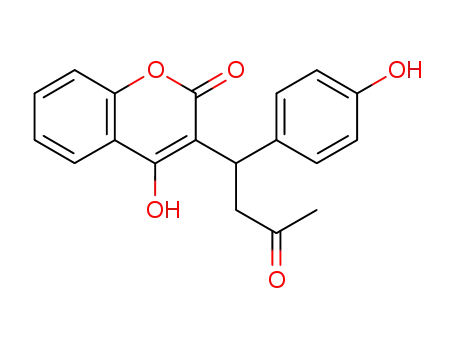
4'-Hydroxywarfarin