Your Location:Home > Products > Pharmaceutical Raw Material > 5-Aminosalicylic acid


CasNo: 89-57-6
MF: C7H7NO3
Appearance: Off-white crystals
|
Description |
5-Aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA), also known as mesalamine, is an anti-inflammatory drug used to treat inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. It's often used to treat mild to moderate cases of IBD, and is considered a "grandfather medication" for colitis. 5-ASA is applied topically to the large intestine's inner lining, or mucous membrane, and can also be taken orally or rectally. |
| Uses | 5-Aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) works by inhibiting the activity of NF-κB, scavenging oxygen free radicals, and affecting the metabolic steps of arachidonic acid. This suppresses the synthesis of prostaglandin and leukotriene, inflammatory mediator, which can help with other inflammatory cascade responses. 5-ASA was originally used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, but was found to help IBD patients during clinical trials. It's been in use since 1942, when it was combined with the antibiotic sulfapyridine to create the molecule sulphasalazine. |
| Indication | It is used for the treatment of active ulcerative proctitis. |
|
Therapeutic Function |
Antibacterial |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Sensitive to moisture. Water insoluble. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
5-Aminosalicylic acid is incompatible with acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, chloroformates and strong oxidizers. |
|
Fire Hazard |
Flash point data for 5-Aminosalicylic acid are not available; however, 5-Aminosalicylic acid is probably combustible. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Nonflammable |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by intraperitoneal route.Moderately toxic by ingestion. Human systemic effects byingestion: hypermotility, diarrhea, dermatitis, increasedbody temperature. When heated to decomposition it emitstoxic fumes of NOx. |
|
Drug interactions |
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs None known |
|
Metabolism |
The absorbed part of mesalazine is almost completely acetylated in the gut wall and in the liver to acetyl-5- aminosalicylic acid. The acetylated metabolite is excreted mainly in urine by tubular secretion, with traces of the parent compound. |
|
Purification Methods |
It crystallises as needles from H2O containing a little NaHSO3 to avoid aerial oxidation to the quinone-imine. The Me ester gives needles from *C6H6, m 96o, and the hydrazide has m 180-182o (from H2O). [Fallab et al. Helv Chim Acta 34 26 1951, Shavel J Amer Pharm Assoc 42 402 1953, Beilstein 14 IV 2058.] |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A monohydroxybenzoic acid that is salicylic acid which is substituted by an amino group at the 5-position. |
|
Brand name |
SALOFALK |
|
General Description |
Odorless white to pinkish crystals or purplish-tan powder. Aqueous solutions acidic (pH approximately 4.1 at 0.8 mg/L water) . |
InChI:InChI=1/C7H7NO3/c8-4-1-2-6(9)5(3-4)7(10)11/h1-3,9H,8H2,(H,10,11)/p-1
The optimal dose to induce remission of ulcerative colitis is 0.5 g 5-aminosalicylic acid 3 times a day. Patients failing with this dose may benefit from an increase of the dose up to 1.0 g 3 times a day, but should also be considered for alternative treatment. A newly developed pellet formulation of 5-aminosalicylic acid has promising efficacy and excellent safety.
Exploring new types of photochemical rea...
Although many therapeutic options are available for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) is still the key medication, particularly for ulcerative colitis (UC). However, the mechanism of action of 5-ASA remains unclear.
hydrogenchloride
![2-hydroxy-5-[1]naphthylazo-benzoic acid](/upload/2024/7/4c127783-4a63-4ce2-8439-ace63167d27b.png)
2-hydroxy-5-[1]naphthylazo-benzoic acid

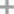
5-Aminosalicylic Acid

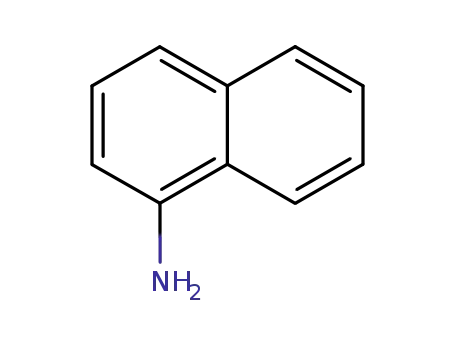
1-amino-naphthalene
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
|
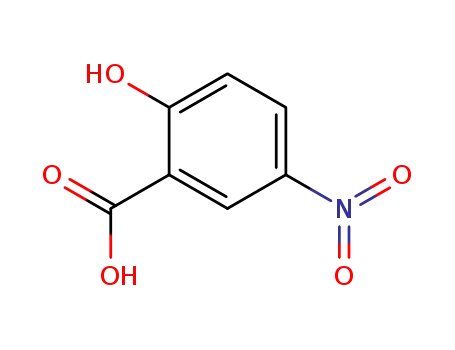
5-nitrosalicylic acid


5-Aminosalicylic Acid

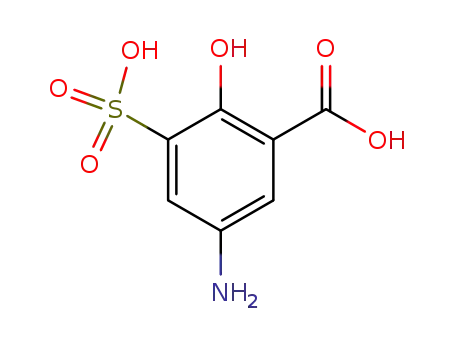
5-amino-2-hydroxy-3-sulfobenzoic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
|
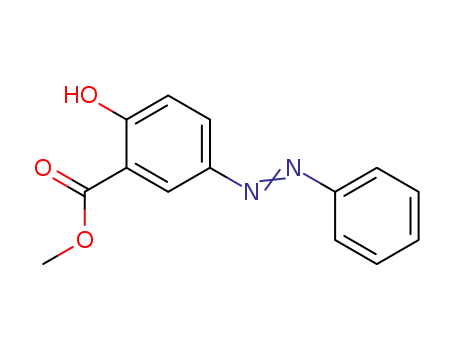
2-hydroxy-5-phenylazobenzoic acid methyl ester

5-nitrosalicylic acid
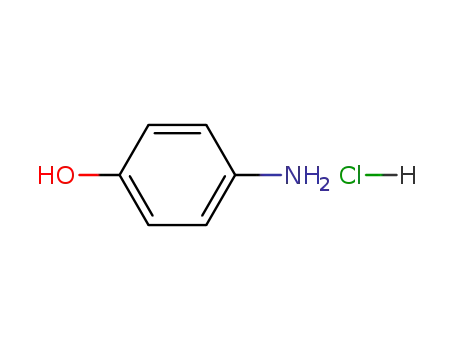
p-aminophenol hydrochloride
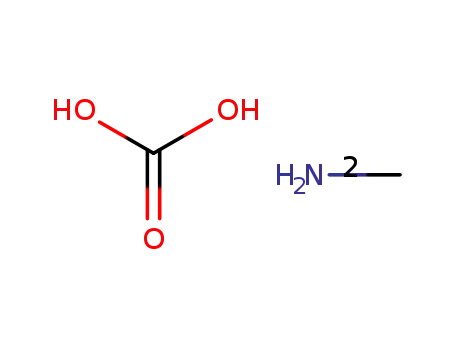
methylammonium carbonate
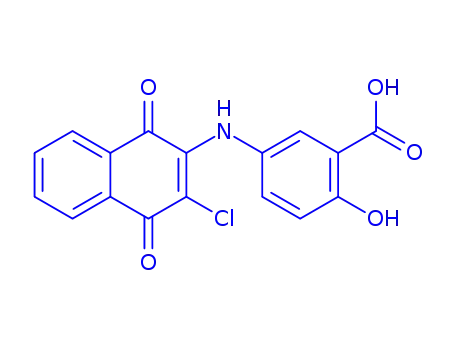
5-(3-chloro-1,4-dioxo-1,4-dihydro-[2]naphthylamino)-2-hydroxy-benzoic acid
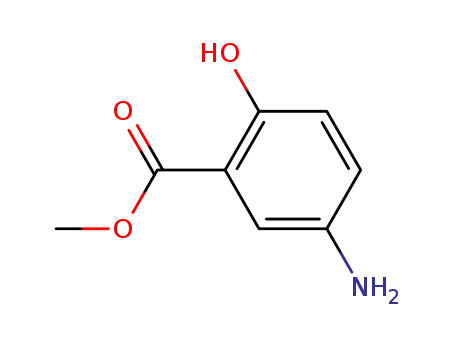
methyl 5-amino-2-hydroxybenzoate
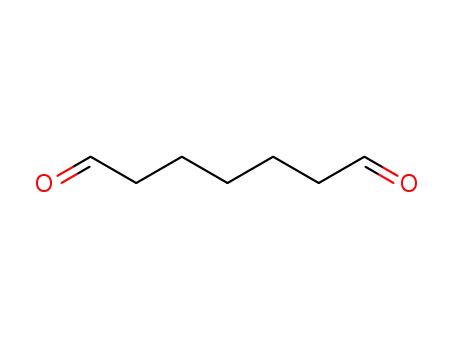
pimelaldehyde
2-hydroxy-5-iodobenzoic acid