Your Location:Home > Products > Pharmaceutical Raw Material > Fluconazole


CasNo: 86386-73-4
MF: C13H12F2N6O
Appearance: white or off white crystalline powder
|
Description |
Fluconazole-D4 is a novel kind triazole drug of anti-fungal infection which was first successfully developed by the American Pfizer with broad-spectrum anti-fungal effect. It belongs to a kind of systemic anti-fungal products and has high selectivity on the inhibitory effect of the fungal cytochrome P450-dependent enzyme. It is also a kind of potent and specific inhibitor for the fungi alcohol synthesis. Fluconazole is used to treat adult neutropenic patients with invasive candidiasis (IC). |
|
Production method |
The synthesis of fluconazole began with an alkylation of a solution of α-chloroketone 5 and 1,2,4-triazole (3, 20 equiv.) to produce intermediate 4. Then, intermediate 4 was reacted with a solution of KOH (22.2 equiv.) |
|
Indications |
Fluconazole (Diflucan) may be better absorbed and is possibly less hepatotoxic than ketoconazole, but it is considerably more expensive, an important consideration given the required length of therapy for most cutaneous fungal diseases. |
|
Manufacturing Process |
It derives from a hydride of a 1H-1,2,4-triazole. Medium: Water; 900 mL for 200 mg/5 mL; 500 mL for 50 mg/5 mL Apparatus 2: 75 rpm Time: 30 min Mobile phase: Methanol and water (40:60). Adjust with glacial acetic acid to a pH of 3.4. |
|
Therapeutic Function |
Antifungal |
|
Antimicrobial activity |
The spectrum is limited, but includes most Candida spp., Cryptococcus spp., dermatophytes and dimorphic fungi (Blast. dermatitidis, Coccidioides spp., Hist. capsulatum and Paracoccidioides brasiliensis). Strains of C. krusei appear to be insensitive. |
|
Biological Activity |
Triazole antifungal agent. Effective against Candida strains in vitro and in vivo . |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Fluconazole is an antifungal agent. It is highly selective inhibitor of fungal cytochrome P-450 sterol C-14 α-demethyllation. Fluconazole is a potent inhibitor of CYP2C9. Fluconazole interferes with fungal ergosterol synthesis and downregulates the metallothionein gene. |
|
Pharmacology |
DIFLUCAN® (fluconazole), the first of a new subclass of synthetic triazole antifungal agents, is available as tablets for oral administration, as a powder for oral suspension, and as a sterile solution for intravenous use in glass and in Viaflex® Plus plastic containers. It has good oral absorption, is well tolerated, and is preferentially taken up in keratinized tissues, reaching concentrations up to 50 times that in plasma. This allows for once-weekly dosing in most cases. Fluconazole is also active in animal infections caused by Blastomyces dermatitidis, Coccidioides immitis, Histoplasma capsulatum, and dermatophytes. |
|
Side effects |
Fluconazole is well tolerated. Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and skin rash have been reported in fewer than 3% of patients. Asymptomatic liver enzyme elevation has been described, and several cases of drugassociated hepatic necrosis have been reported. Alopecia has been reported as a common adverse event in patients receiving prolonged high-dose therapy. Coadministration of fluconazole with phenytoin results in increased serum phenytoin levels. |
|
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments |
Fluconazole may have use in veterinary medicine in the treatment of systemic mycoses, including cryptococcal meningitis, blastomycosis, and histoplasmosis. It may also be useful for superficial candidiasis or dermatophytosis. Because of the drug’s unique pharmacokinetic qualities, it is probably more useful in treating CNS infections or fungal urinary tract infections than other azole derivatives. Fluconazole does not have appreciable effects (unlike ketoconazole) on hormone synthesis and may have fewer side effects than ketoconazole in small animals. |
|
Metabolism |
Fluconazole is metabolised only to a minor extent. Of a radioactive dose, only 11% is excreted as metabolites in the urine. The major route of excretion is renal, with approximately 80% of the administered dose appearing in the urine as unchanged medicinal product. Fluconazole clearance is proportional to creatinine clearance. There is no evidence of circulating metabolites. |
|
Brand name |
Diflucan (Pfizer). |
InChI:InChI=1/C13H12F2N6O/c14-10-1-2-11(12(15)3-10)13(22,4-20-8-16-6-18-20)5-21-9-17-7-19-21/h1-3,6-9,22H,4-5H2
While many mechanisms of resistance observed in C. albicans are also found in the non-albicans species, there are also important and unexpected differences between species. Furthermore, mechanisms of fluconazole resistance in emerging Candida spp., including the global health threat Candida auris, are largely unknown.
The application of continuous methods in...
Fluconazole and a series of 2-(2,4-diflu...
Adults with invasive candidiasis were randomly assigned to receive either intravenous anidulafungin or intravenous fluconazole. All patients could receive oral fluconazole after 10 days of intravenous therapy. The primary efficacy analysis assessed the global response (clinical and microbiologic) at the end of intravenous therapy in patients who had a positive baseline culture. Efficacy was also assessed at other time points.
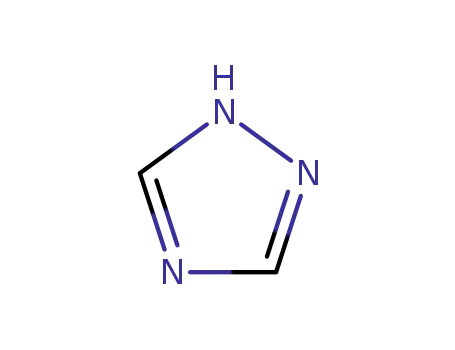
1,2,4-Triazole
![1-[2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-2,3-epoxypropyl]-1H-1,2,4-triazole](/upload/2024/7/09bd1e5a-d35f-4af3-b4cf-f3e38ea203d5.png)
1-[2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-2,3-epoxypropyl]-1H-1,2,4-triazole

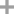
fluconazole
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With potassium carbonate; In acetonitrile; at 60 ℃;
|
68.1% |
|
With potassium carbonate; In isopropyl alcohol; at 75 ℃; for 16h;
|
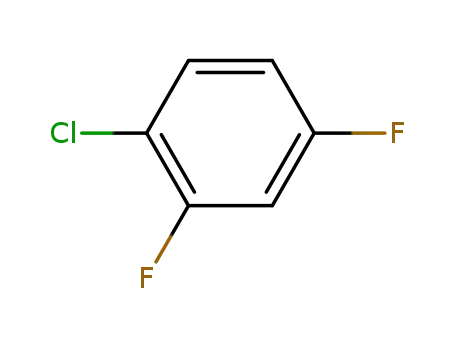
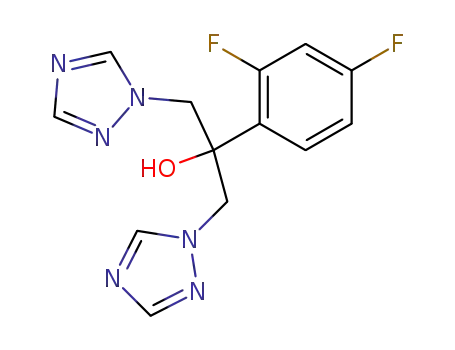
1-chloro-2,4-difluorobenzene

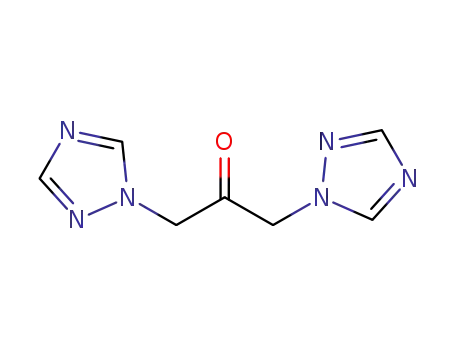
1,3-bis(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propanone


fluconazole
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
1-chloro-2,4-difluorobenzene; With iodine; magnesium; lithium chloride; In 2-methyltetrahydrofuran; at 40 - 50 ℃; for 3h;
1,3-bis(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propanone; In 2-methyltetrahydrofuran; at 20 - 40 ℃; for 2h;
|
96.1% |

1,2,4-Triazole
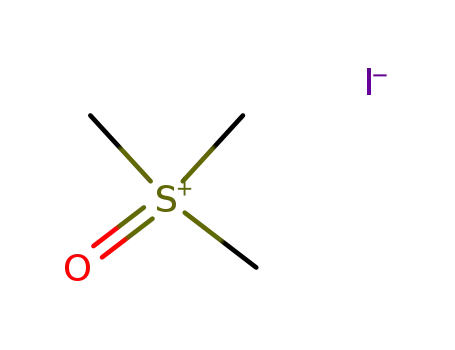
trimethylsulfoxonium iodide
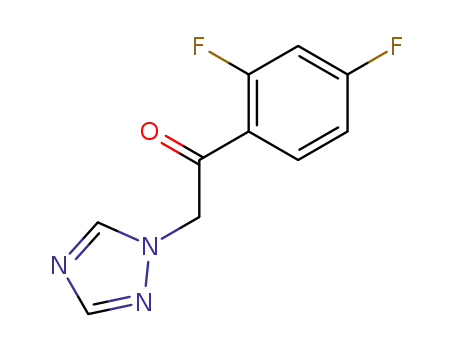
1-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazolyl)ethanone
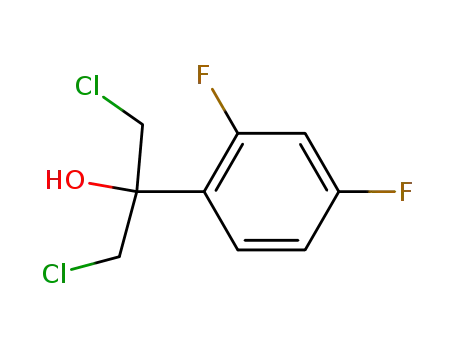
1,3-(dichloro)-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)propan-2-ol
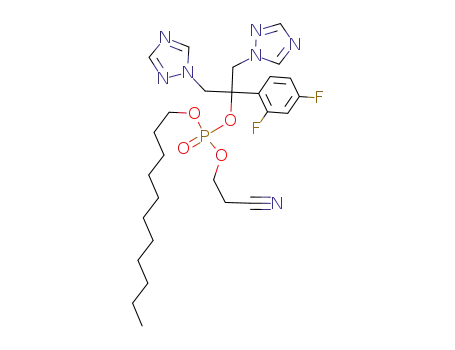
2-cyanoethyl-n-undecanyl fluconazole phosphate
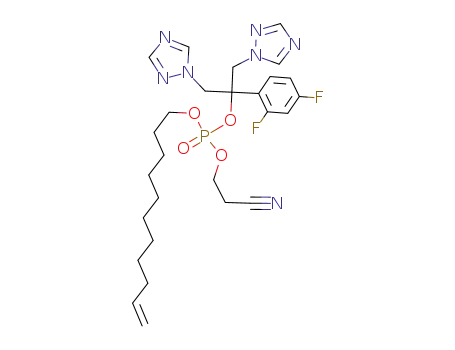
2-cyanoethyl-ω-undecenyl fluconazole phosphate
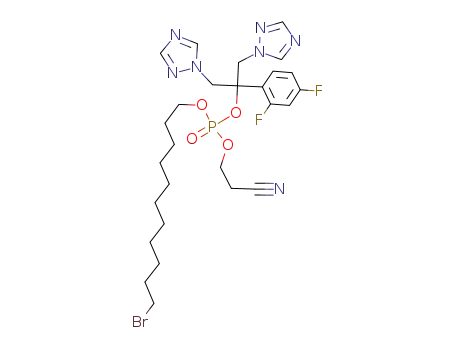
11-bromoundecanyl-2-cyanoethyl fluconazole phosphate